4.5 Electromagnetic effects
4.5.5 The d.c. motor
Core Content
Current-carrying coil in a magnetic field
- A coil carrying a current in a magnetic field experiences a turning effect.
- The turning effect causes the coil to rotate.
Turning effect can be increased by:
- (a) Increasing the number of turns on the coil
- (b) Increasing the current
- (c) Increasing the strength of the magnetic field
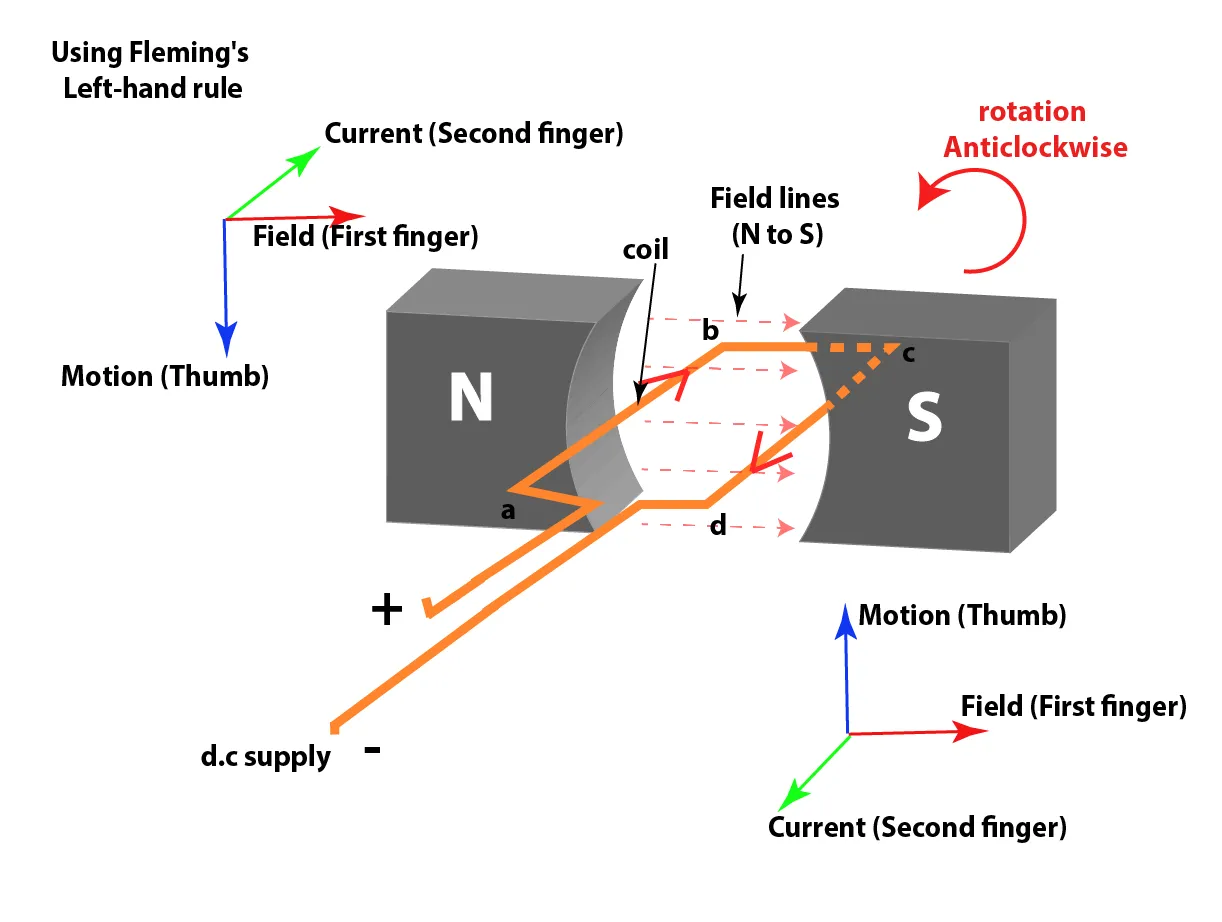
Figure 1: A single coil in a magnetic field
Supplement Content
Operation of a Simple d.c. Motor
- The directions of the forces on the coil are determined using Fleming's Left-Hand Rule (motor rule).
- Current in one side of the coil (e.g., side ab) experiences a force upwards.
- Current in the other side of the coil (e.g., side cd) experiences a force downwards.
- These opposite forces cause the coil to rotate.
Role of the Split-Ring Commutator and Brushes:
- The split-ring commutator reverses the direction of the current every half turn.
- This ensures that the coil continues to rotate in the same direction.
- The brushes are fixed and maintain contact with the rotating commutator.
Additional details:
- When the coil is vertical, there is no force acting on it because the contacts are at the gap in the split ring.
- The coil continues to rotate due to its momentum until the forces act again.
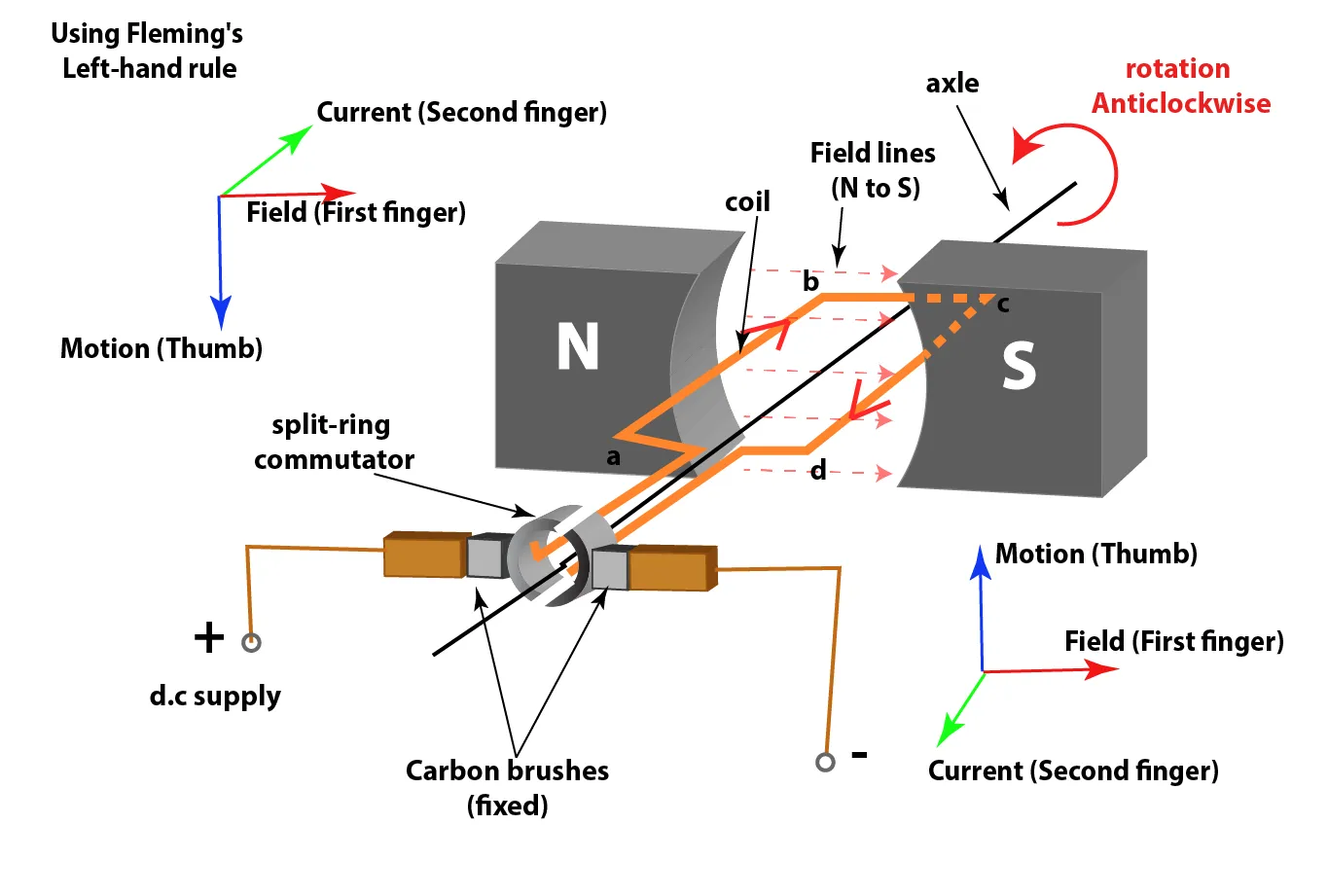
Figure 2: Operation of an electric motor, including the action of a split-ring commutator and brushes
Practice Questions
Q1. Figure 1.1 shows a horizontal, flat coil in a magnetic field
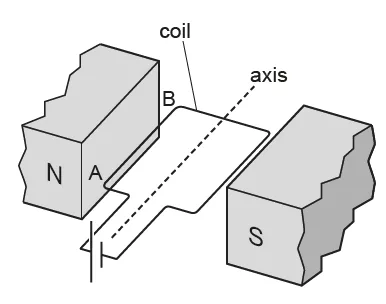
Figure 1.1
The coil is connected to a cell. The coil rotates.
(a) Determine the direction of movement of the side AB relative to the plane of the coil.
direction of movement = ......................................................... [1]
(b) Explain how you determined the direction in (a).
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(c) State and explain what happens to the coil as it reaches the vertical position.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(d) To operate as a motor, a split‑ring commutator and brushes are added to the parts shown in Fig. 1.1.
Explain the effects of the split‑ring commutator and the brushes on the action of the motor.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [3]
Total: 8 marks
Q1
(a) downwards / into the page / anti-clockwise [1]
(b) current, (magnetic) field, motion at right angles to each other [1]
magnetic field from left to right / N to S AND current is from A to B / positive to negative [1]
(c) (at vertical) the coil stops OR (at vertical) the coil overshoots and comes back OR the coil vibrates (about the vertical) [1]
any one from:
- (as the coil approaches vertical) the turning effect decreases
- (at vertical) the turning effect is zero
- (past vertical) the turning effect reverses / changes direction
[1]
(d) reverses the current [1]
any two from:
- (brushes) ensure current is maintained
- coil rotates continuously / continues to move in the same direction
- (allows current to change direction) without wires getting tangled
- (reverses the current) every half turn / 180 degrees / OR (reverses the current) when the coil is vertical / at right angles to the magnetic field
[2]
IGCSE Physics | The DC Motor
