1.4 Density
density can be defined as “mass per unit volume”
$$ ρ={{m}\over{V}}$$
ρ = Density
m = Mass (Kg or g)
V = Volume
$$Unit\;of\;density\;can\;be\;Kg/m^{3}\;or\;g/cm^{3}$$
Describe how to determine the density of a liquid,
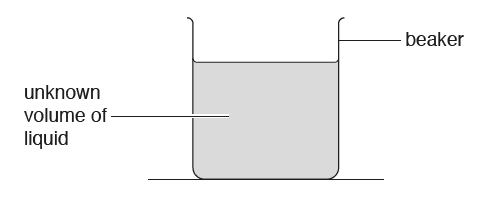
Step 01 : Measure mass of empty measuring beaker using a balance
Step 02 : Add measured/fixed volume of liquid to the beaker.(You can measure the volume of the liquid using a measuring cylinder)
Step 03 : Measure mass of measuring beaker and liquid
Step 04 : Determine mass of liquid (by subtracting mass empty from mass when full)
Step 05 : Use of the equation to find out Density.
$$ ρ={{m}\over{V}}$$
Describe how to determine the density of a regularly shaped solid,
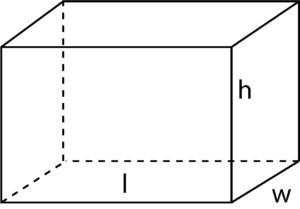
Step 01 : Find the mass of the object using a balance
Step 02 : Find the volume using the following equation,
Volume (V) = Length (l) x Width (w) x Height (h)
Step 03 : Use of the equation to find out Density
$$ ρ={{m}\over{V}}$$
Describe how to determine the density of an irregularly shaped solid.
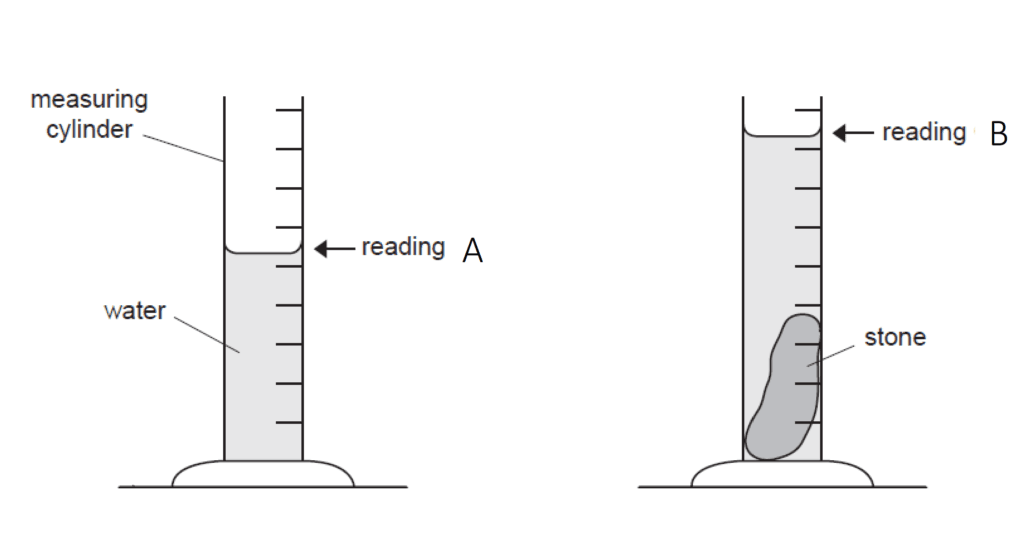
Step 01 : Measure the mass of the stone using a balance
Step 02 : Fill the measuring cylinder with water to a known volume.(Reading A)
Step 03 : Solid body immersed in water present in the measuring cylinder.
Step 04 : Volume of irregular solid = Final volume – Initial volume
Step 05 : Use of the equation to find out Density
$$ ρ={{m}\over{V}}$$
Determine whether an object floats based on density data:
- An object will float if its density is less than the density of the liquid it is placed in.
- If the object’s density is greater than the liquid’s density, it will sink.
- Example: If an object has a density of 0.8 g/cm³ and the liquid’s density is 1.0 g/cm³, the object will float.
Determine whether one liquid will float on another liquid (given they do not mix):
- A liquid with a lower density will float on top of a liquid with a higher density if they do not mix.
- Example: Oil (density ≈ 0.9 g/cm³) will float on water (density ≈ 1.0 g/cm³) because oil is less dense.
