1.2 Motion
Speed
Speed is the distance travelled per unit time.
$$s={{d}\over{t}}$$
‘S’ = speed (m/s or km/hr)
‘d’ = Distance (m or km)
‘t’ = time (s or hr)
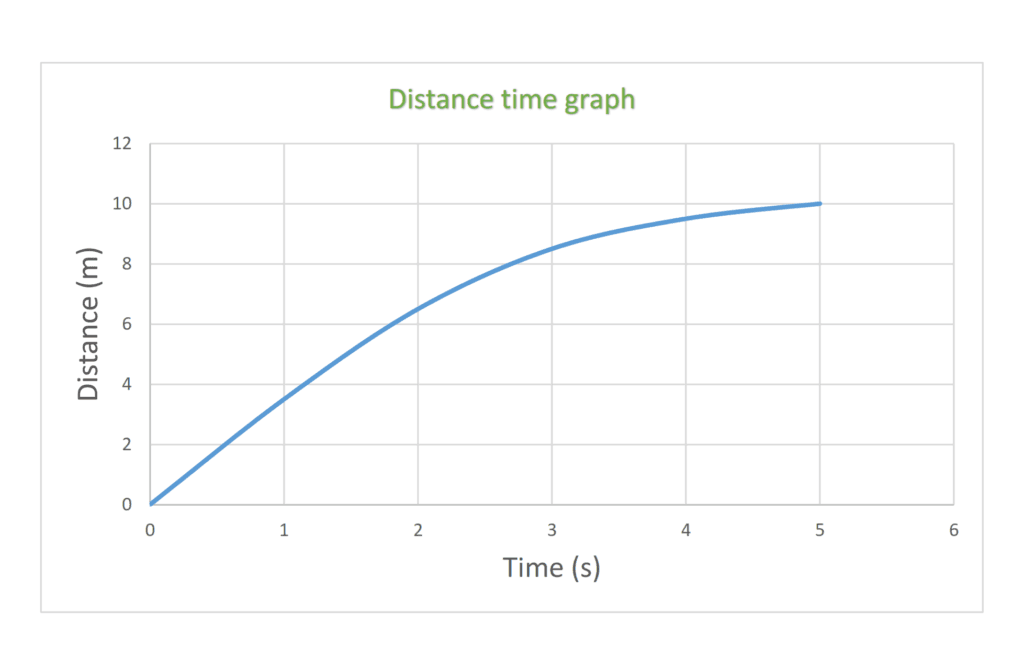
Distance Time Graph
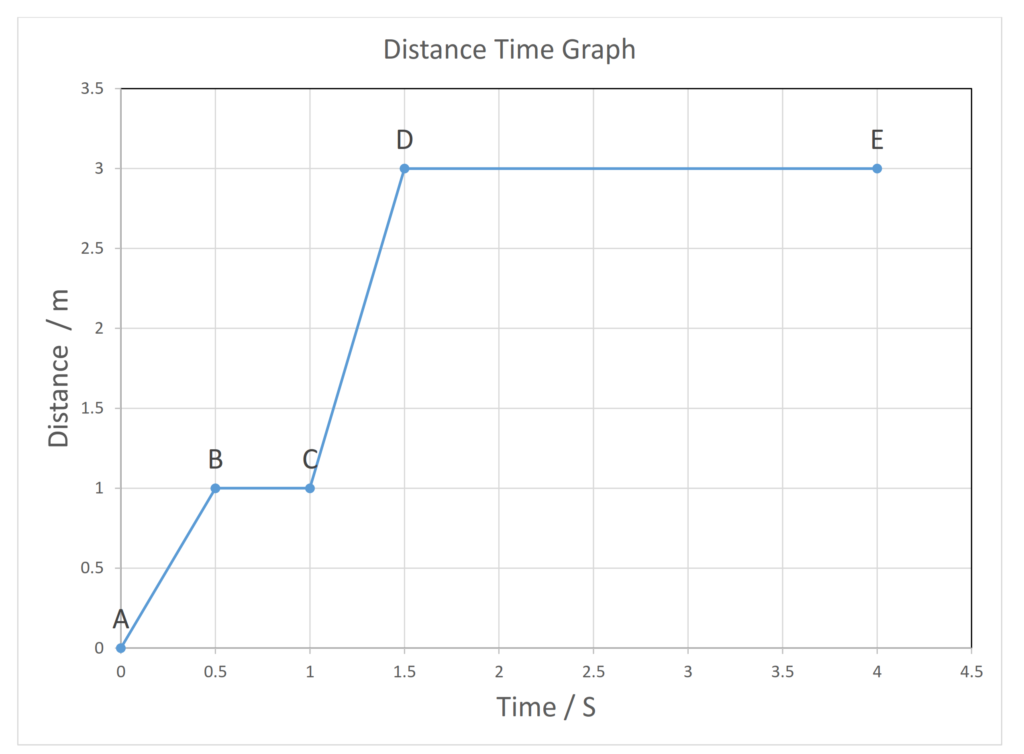
- A – B Distance traveled = 1m, and Time taken = 0.5 S
- B – C Distance traveled = 0m, and Time taken = 0.5 S
- C – D Distance traveled = 2m, and Time taken = 0.5 S
- D – E Distance traveled = 0m, and Time taken = 2.5 S
- Total Distance traveled = 3m
Distance time graphs. If an object moves along a straight line, the distance travelled can be represented by a distance-time graph.
On a distance time graph, the gradient of the line is equal to the speed of the object.

- Determine, qualitatively, from given data or the shape of a distance–time graph when an object is:
(a) at rest
(b) moving with constant speed
(c) accelerating
(d) decelerating
(a) at rest
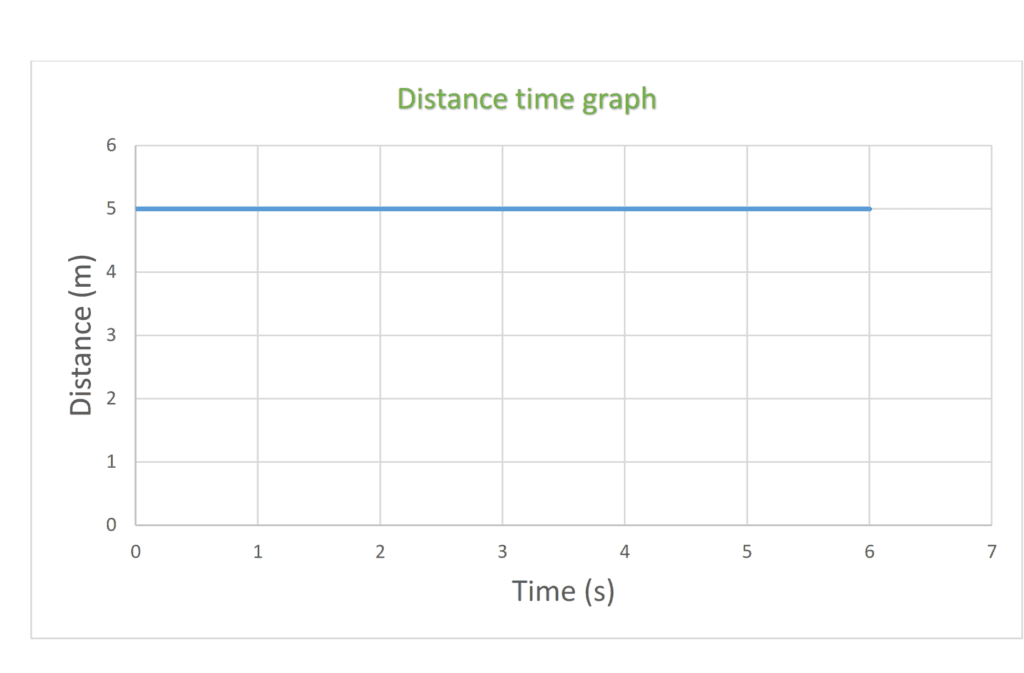
(b) moving with constant speed
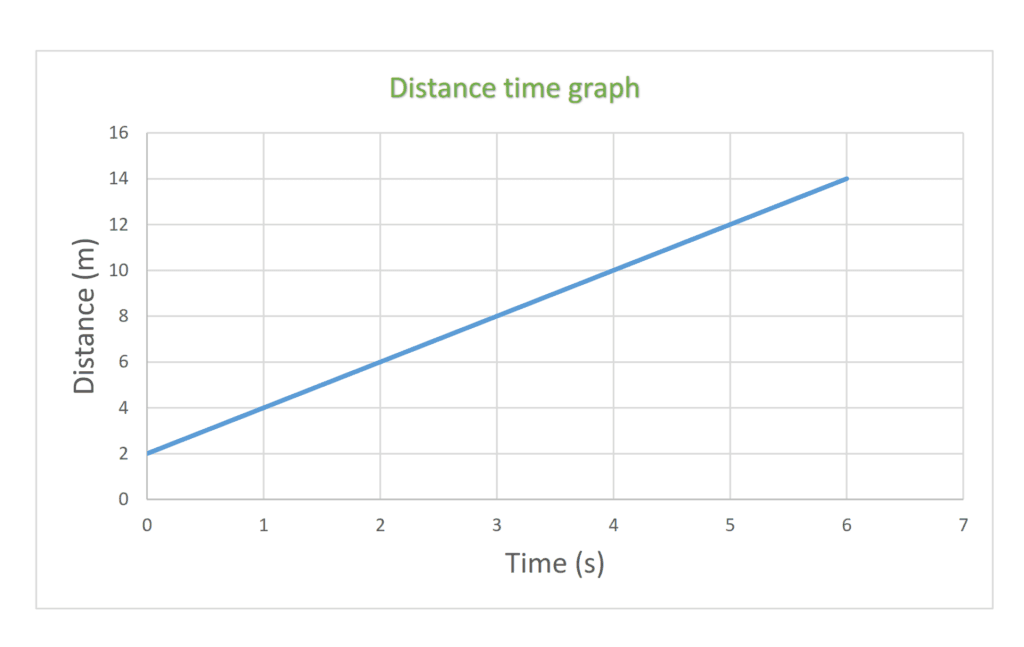
(c) accelerating
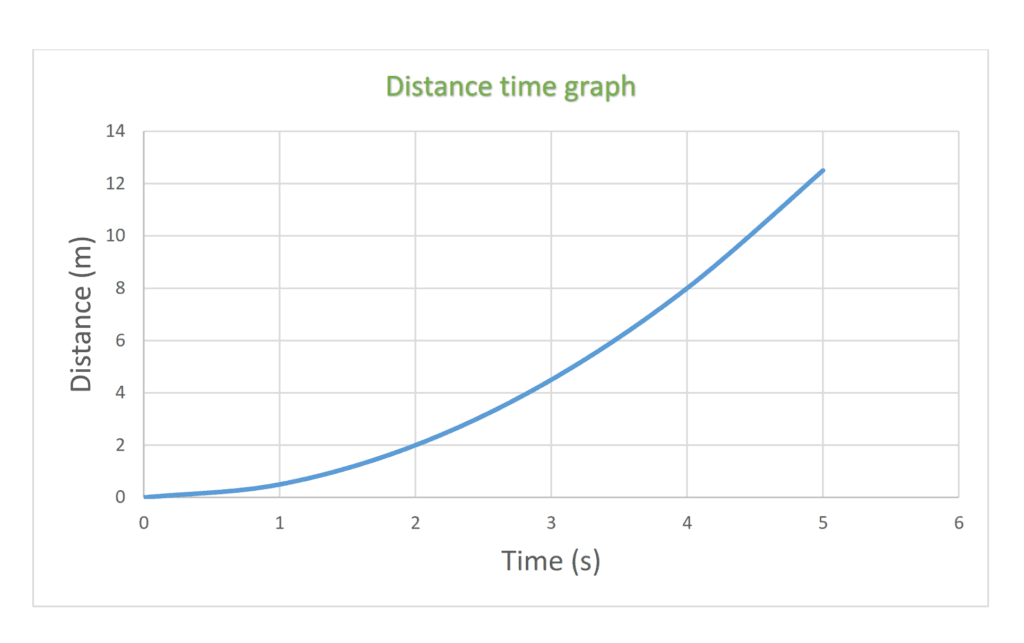
(d) decelerating
Speed Time Graph
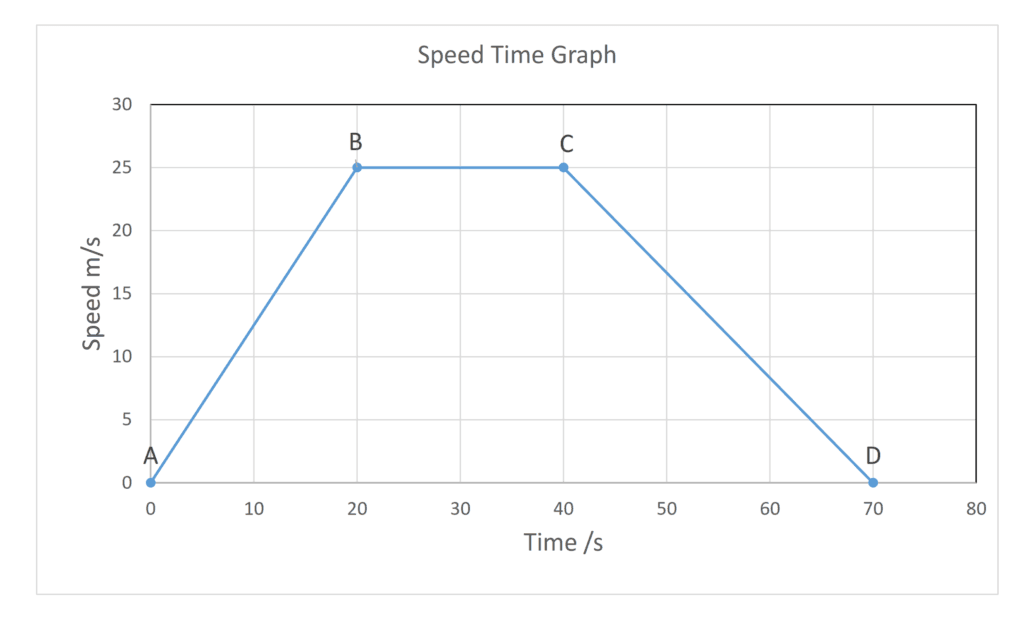
A lorry is moving in traffic and its motion is shown below
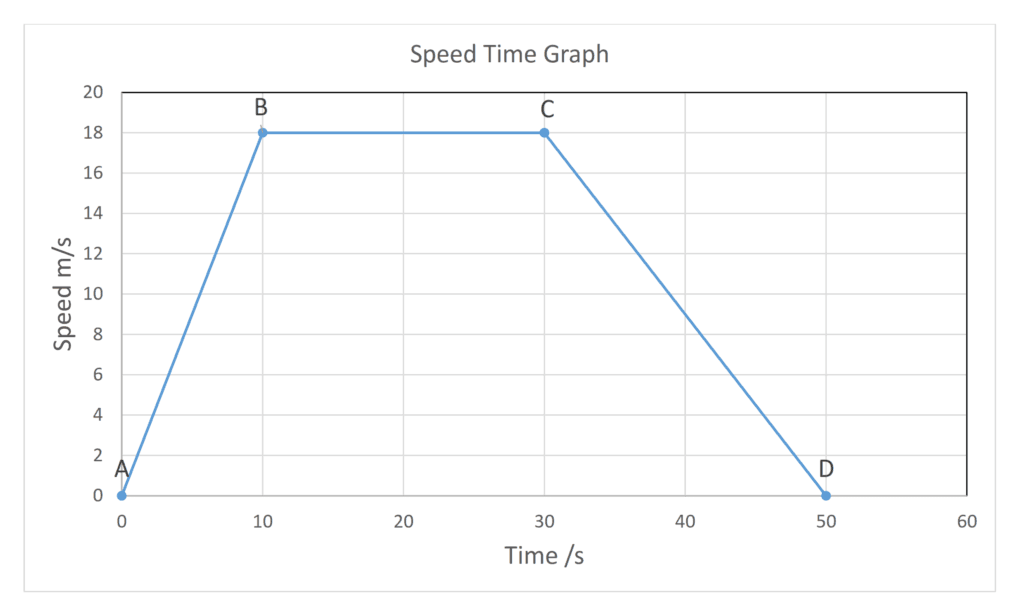
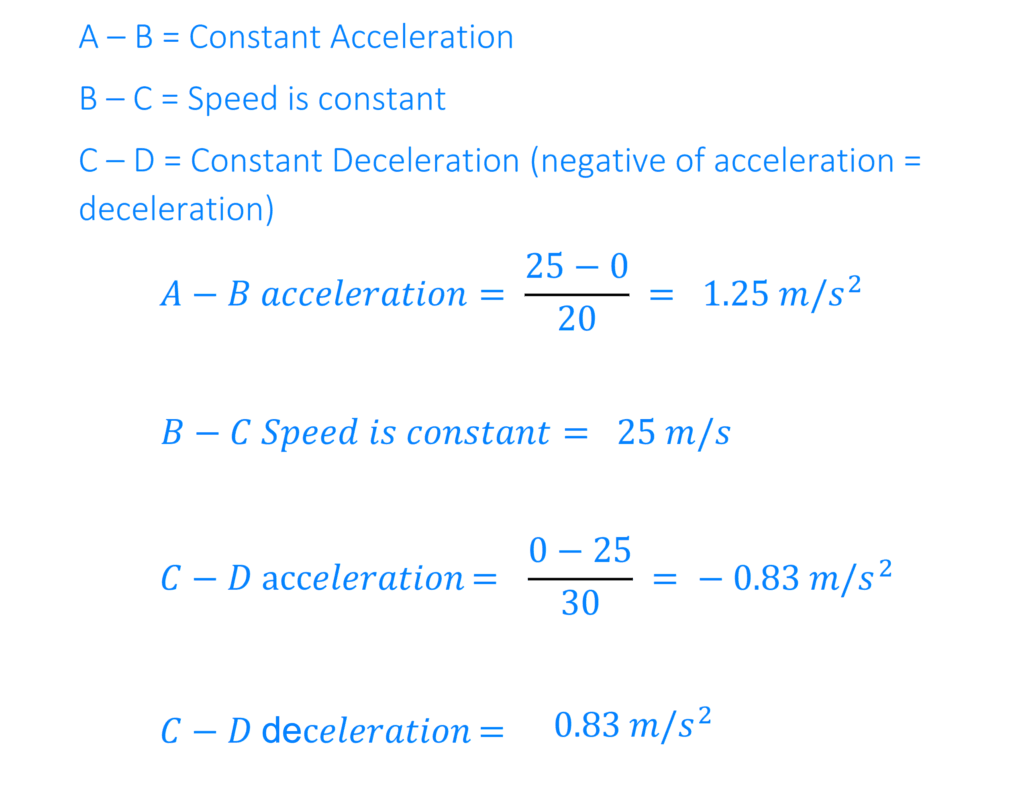
- A – B = Acceleration
- B – C = Steady Speed / Constant Speed / Uniform Speed
- C – D = Deceleration
- Speed Time Graphs show the speed of an object over time.
- The Area under the speed time graph is the distance traveled
Therefore, total distance traveled by the lorry is:

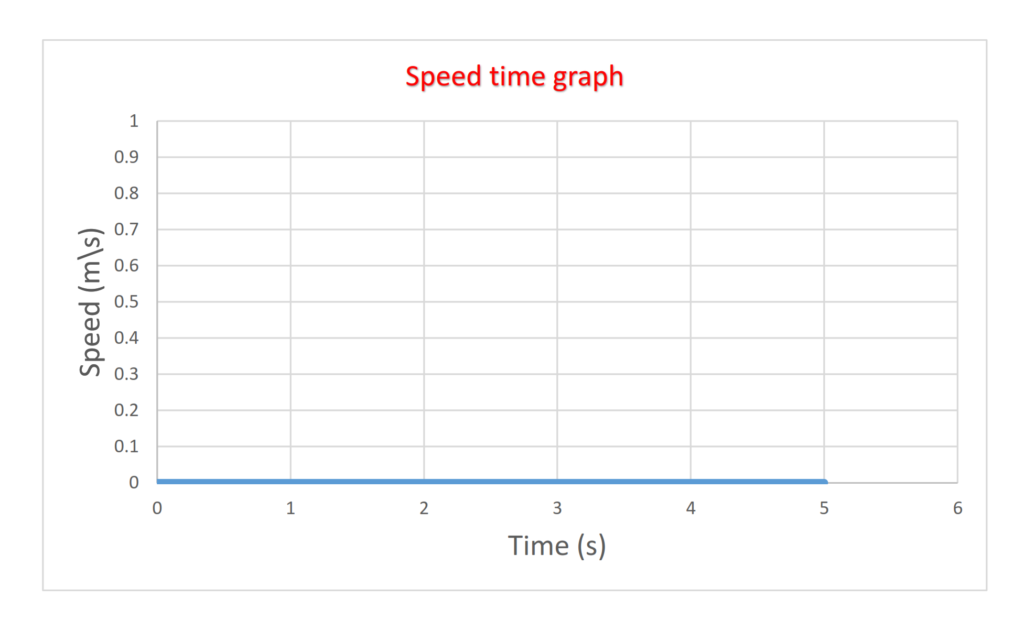
- When a speed time graph is at rest the line meets the x – axis.
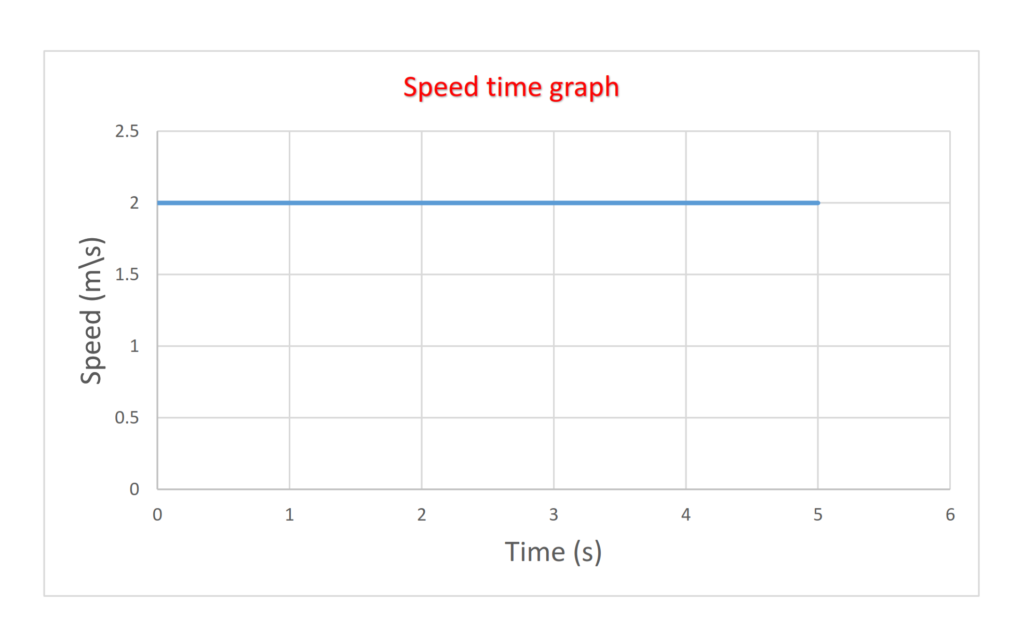
- When an object moves with a constant speed we draw the line parallel to the x – axis.
- When the object moves with a changing speed the line slopes.
- Determine, qualitatively, from given data or the shape of a speed–time graph when an object is:
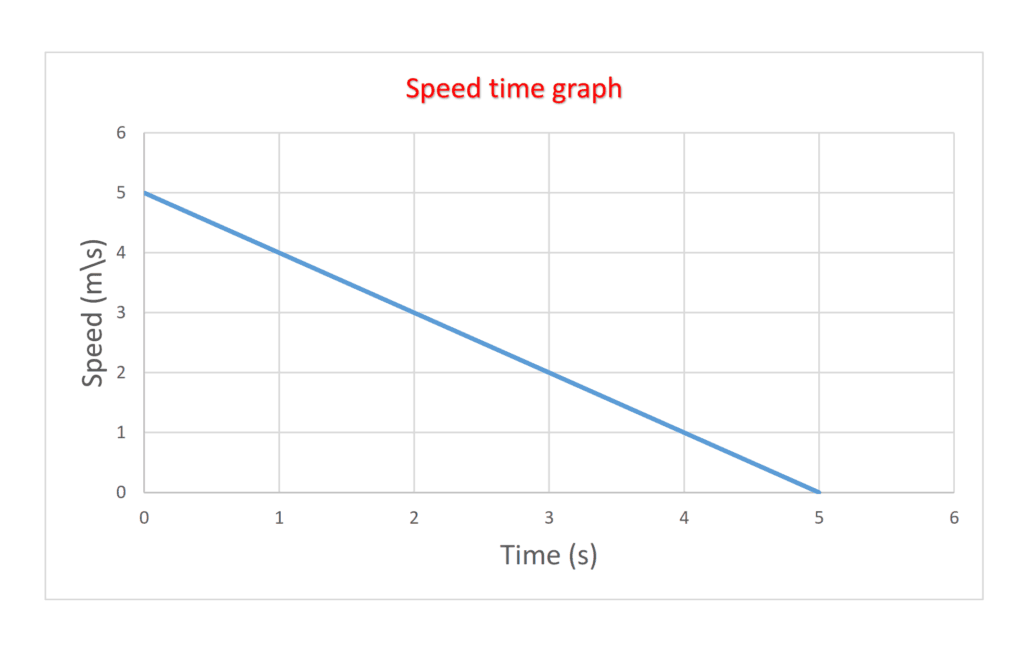
(a) at rest
(b) moving with constant speed
(c) accelerating
(d) decelerating
(a) at rest
(b) moving with constant speed
(c) accelerating
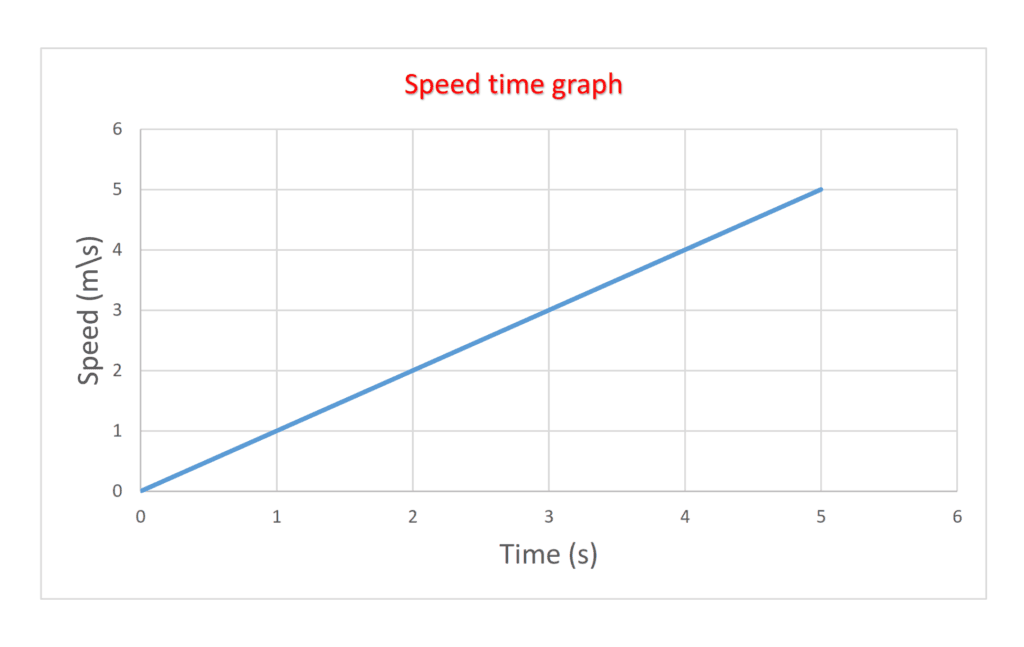
(d) decelerating
Velocity
Velocity is a vector quantity & Speed is a scalar quantity
Velocity is the rate of change in displacement. (or. Speed in a specific Direction)
$$v={{d}\over{t}}$$
‘v’ = velocity (m/s or km/hr)
‘d’ = Displacement (m or km)
‘t’ = time (s or hr)
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity.
Acceleration of free fall for a body near to the Earth is constant.
$$a={{v-u}\over{t}}$$
‘a’ = acceleration
‘u’ = initial velocity
‘v’ = final velocity
‘t’ = time (s )
$$Unit\;of\;acceleration\;=\;ms^{-2}$$
- Determine from given data or the shape of a speed–time graph when an object is moving with:
(a) Constant acceleration
(b) Changing acceleration
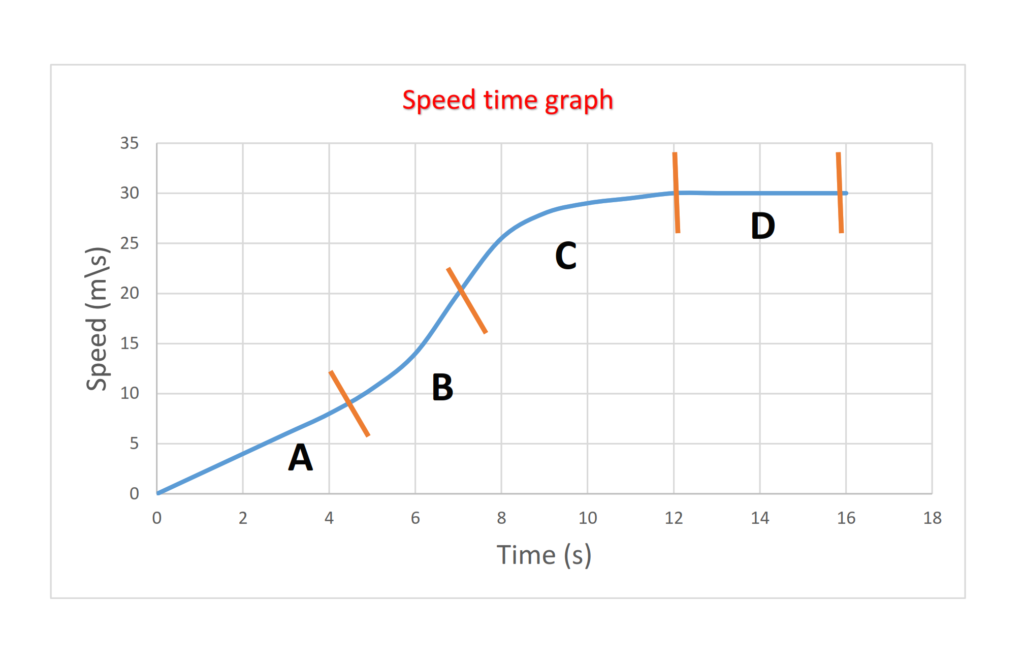
A = Constant acceleration
B = Increasing acceleration
C = Decreasing acceleration
D = zero acceleration or constant speed
Terminal Velocity
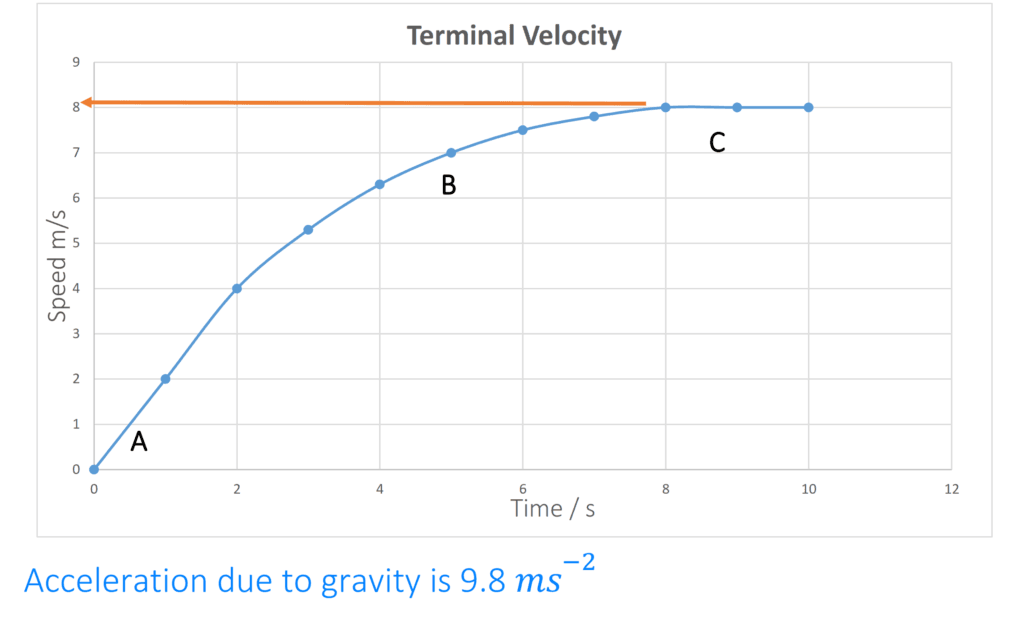
However, objects do not maintain this acceleration(acceleration due to gravity) in air because air resistance acts upwards.
At point A in above figure the speed is slow so there is negligible air resistance and the body has free fall acceleration.
At point B, the speed is higher and there is some air resistance, so acceleration is less than free fall.
At point C, the body has high speed and high air resistance, which is equal to its weight. Therefore, there is no acceleration, this constant speed is called Terminal Velocity

Where’s d-t picture